Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > GEO DATA > Volume 5(2); 2023 > Article
-
Original Paper
위성 부가산출물 검증을 위한 나주 지상관측사이트 관측 자료 및 웹 서비스 소개 -
하종성1
 , 정승택1
, 정승택1 , 김현옥2
, 김현옥2 , 이선구3
, 이선구3 , 정대원4
, 정대원4 , 조재일5,*
, 조재일5,* , 신서호6
, 신서호6 , 김길자7
, 김길자7 , 김동관8
, 김동관8 , 염종민9,*
, 염종민9,*
- The Introduction of Naju Ground Observation Site Measurement Data and Web Service for Validation of Satellite Value-Added Products
-
Jong-Sung Ha1
 , Seung-taek Jeong1
, Seung-taek Jeong1 , Hyun-Ok Kim2
, Hyun-Ok Kim2 , Sun-Gu Lee3
, Sun-Gu Lee3 , Dae-won Jeong4
, Dae-won Jeong4 , Jaeil Cho5,*
, Jaeil Cho5,* , Seo Ho Shin6
, Seo Ho Shin6 , Kil-Ja Kim7
, Kil-Ja Kim7 , Dong-Kwan Kim8
, Dong-Kwan Kim8 , Jong-Min Yeom9,*
, Jong-Min Yeom9,*
-
GEO DATA 2023;5(2):103-109.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2023.0012
Published online: June 27, 2023
1선임연구원, 한국항공우주연구원 위성활용부, 대전광역시 유성구 과학로 169-84, 34133, 대한민국
2책임연구원, 한국항공우주연구원 위성활용부, 대전광역시 유성구 과학로 169-84, 34133, 대한민국
3부장, 한국항공우주연구원 위성활용부, 대전광역시 유성구 과학로 169-84, 34133, 대한민국
4센터장, 한국항공우주연구원 위성활용부, 대전광역시 유성구 과학로 169-84, 34133, 대한민국
5부교수, 전남대학교 응용식물학과, 광주광역시 북구 용봉로 77, 61186, 대한민국
6연구원, 전라남도농업기술원 식량작물연구소, 전라남도 무안군 삼향읍 오룡길 1, 58564, 대한민국
7팀장, 전라남도농업기술원 식량작물연구소, 전라남도 무안군 삼향읍 오룡길 1, 58564, 대한민국
8소장, 전라남도농업기술원 식량작물연구소, 전라남도 무안군 삼향읍 오룡길 1, 58564, 대한민국
9부교수, 전북대학교 지구환경과학과, 전라북도 전주시 덕진구 백제대로 567, 54896, 대한민국
1Senior Researcher, Satellite Application Division, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, 169-84 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, 34133 Daejeon, South Korea
2Principal Researcher, Satellite Application Division, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, 169-84 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, 34133 Daejeon, South Korea
3Director, Satellite Application Division, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, 169-84 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, 34133 Daejeon, South Korea
4Executive Director, Satellite Application Division, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, 169-84 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, 34133 Daejeon, South Korea
5Associate Professor, Applied Plant Science, Chonnam National University, 77 Yongbong-ro, Buk-gu, 61186 Gwangju, South Korea
6Researcher, Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research & Extension Services, 1 Oryong-gil, Samhyang-eup, Muan-gun, 58564 Jeollanam-do, South Korea
7Team Leader, Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research & Extension Services, 1 Oryong-gil, Samhyang-eup, Muan-gun, 58564 Jeollanam-do, South Korea
8Director, Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research & Extension Services, 1 Oryong-gil, Samhyang-eup, Muan-gun, 58564 Jeollanam-do, South Korea
9Associate Professor, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Jeonbuk National University, 567 Baekje-daero, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju, 54896 Jeollabuk-do, South Korea
- Corresponding Author Jong-Min Yeom Tel: +82-63-270-3350 E-mail: jmyeom@jbnu.ac.kr
- *Equal correspondence goes to this author.
Copyright © 2023 GeoAI Data Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 524 Views
- 33 Download
Abstract
- The Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) has collaborated with Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research & Extension Services and Chonnam National University to establish a ground observation tower for evaluating the value-added products (such as surface reflectance and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) and improving algorithms of domestic development satellites (Korea Multi-Purpose Satellite-3, 3A and 7). The ground measurement tower, installed at the Jeollanamdo Naju ground observation site (NGOS), constantly observes surface hyperspectral reflectance and atmospheric information, providing the advantage of real-time algorithm validation improvement when satellite acquires images of the site. The NGOS operates hyperspectral radiometer equipment (6 types), meteorological observation equipment (5 types), sky radiometer (1 type), and eddy flux observation equipment (2 types), along with a web service for display and data processing. The ground observation site equipment that is being installed and operated can be utilized in various fields such as carbon circle, agriculture, environment, atmosphere and climate change, in addition to validation of satellite value-added products. This study aims to introduce KARI NGOS for user data sharing and highlight the characteristics of the measured data.
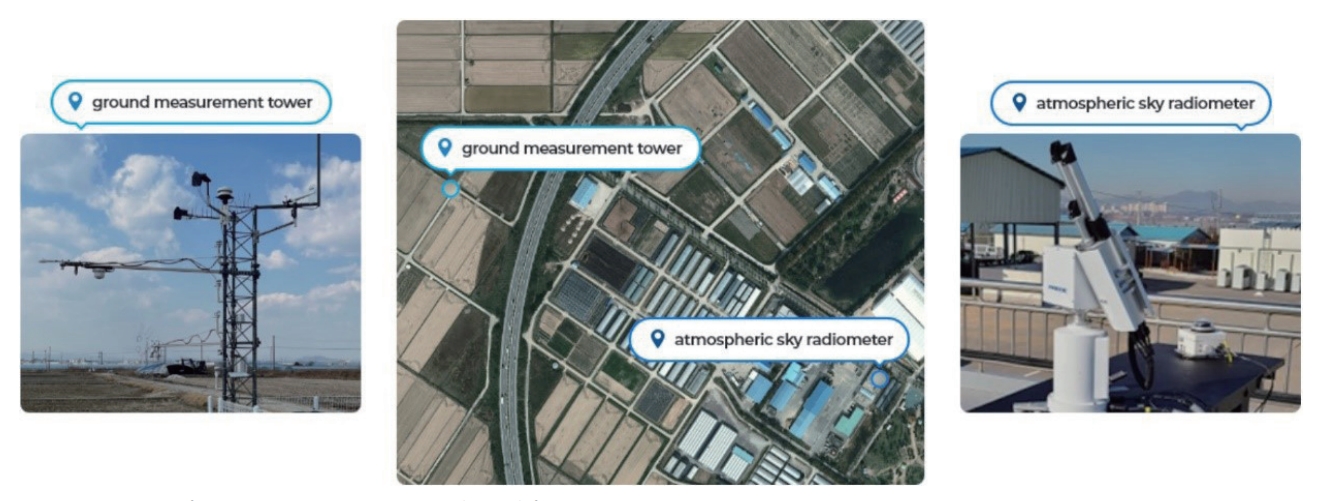
- 최근 뉴스페이스(new space) 시대에 따른 우주개발 경쟁은 전 세계적으로 치열해지고 있다. 우리나라는 우주개발진흥 기본계획에 따라, 다목적 실용위성 시리즈를 포함한 초소형위성 군집시스템(11기)을 개발 중이다. 이는 국가에서 활용 가능한 위성의 수도 급속도로 증가한다는 의미를 가진다. 또한, 다른 의미에서 국가에서 품질관리를 해야 할 위성의 수 또한 증가되었다는 것이다. 검교정 장비를 장착하지 못한 위성은 관측 특성상 궤도면에 진입 이후에는 위성센서의 복사 정확도를 자체적으로 개선하는 것은 쉽지 않다. 다만, 위성 탑재 검교정 장치(onboard absolute radiometric calibrator)를 이용하여 절대복사보정이 가능하지만 비용이 상당할 뿐만 아니라, 최근 위성 초소형화 추세와도 맞지 않다. 전통적인 현장관측(field campaign)을 통해 위성의 복사 및 부가 산출물 품질을 개선할 수 있지만, 현재 위성 군집시스템 개발 상황에서는 비용과 효율성 문제가 제기된다. 따라서, 최근에는 우주개발선진국에서는 지상관측타워를 설치하여 자국 위성의 복사 및 부가산출물 품질 개선을 수행하고 있다(Xu et al., 2019). 왜냐하면 지상관측타워는 균질성을 가지는 특정 피복 위에 설치되어 초분광 반사도, 대기복사, 생태환경 변수 및 기상을 상시적으로 관측함으로써, 위성이 지상관측사이트를 관측하면 현장관측 자료와 연동하여 자동으로 품질평가 및 알고리즘 개선이 가능하기 때문이다. 즉, 증가되는 위성의 수와 상관없이 상시적으로 위성의 성능을 지상에서 검증이 가능하다는 장점이 있다. 한국항공우주연구원(이하 항우연), 전남농업기술원, 전남대학교는 2020년 6월 기관 간 MOU (memorandum of understanding) 체결을 통해 위성 부가 산출물 검증용 지상관측사이트를 나주에 구축하였다. 지상관측사이트에 대한 현장관측은 2020년 1월부터 현재까지 상시적으로 관측 중이다. 지상관측사이트 관측 지점은 Fig. 1과 같이 위도 35.027° N, 경도 126.822° E, 전남농업기술원(전라남도 나주시 소재) 벼 시험포장에 위치하고 있다. 지상관측 사이트에는 초분광 관측장비, 기상관측장비, 대기복사계, 스카이 카메라, 에디 플럭스(eddy flux) 관측장비가 전남농업 기술원 시험논 부지 내 각각 설치되어 있다(Fig. 1). 지상관측 사이트에 대한 정밀대기복사를 관측하기 위한 POM-02 대기관측 지점(point of atmospheric sky radiometer)과 지상관측타워가 설치되어 있는 지상관측 타워 지점(point of ground measurement tower)으로 나눠 진다. 실제 두 지점 간의 거리 차이는 550 m 이내로, 대기관측 지점에서 관측한 대기정보(에어러솔 광학 두께, 수증기량 및 오존)를 지상관측 타워 지점에 적용하기에는 큰 무리가 없다.
- 항우연에서는 지상관측사이트에서 제공되는 초분광 지표 반사도와 대기 정보(에어러솔 광학 두께, 수증기량, 오존량)를 이용하여 다목적 실용위성과 초소형 위성에 대한 부가산출물(지표반사도 및 정규식생지수)에 대한 상시 품질검증에 활용할 계획이다. 즉, 정밀대기복사계 관측 자료를 이용하여 다목적 실용위성 혹은 초소형 위성에 대한 대기보정을 수행한다. 이후, 대기보정된 위성 지표반사도 값과 지상관측타워에서 관측되는 fluorescence box (FLOX) 초분광관측 반사도 자료를 이용하여, 위성의 spectral response function 내 반사도로 변환하여 비교·분석할 예정이다. 따라서 항우연에서 운영 중인 위성군이 나주 지상관측사이트 지역을 관측하게 되면 자동으로 각 부가산출물 정확도 비교·분석이 가능하다. 뿐만 아니라, 차세대 중형위성 1호, 2호, 4호 그리고 국내 산업체에서 자체적으로 개발한 초소형 위성군에 대한 품질 정보 감시 업무 지원도 가능하다.
1. 서론
- 앞에서 언급한 바와 같이, 지상관측사이트에서는 크게 지표 초분광반사도를 측정하는 초분광계, 지표피복의 탄소순환 및 기상관측(지상관측 타워 지점) 그리고 대기복사를 측정하는 대기복사계 및 스카이 카메라 관측(대기관측 지점)으로 나눠진다. 보다 구체적인 각 장비에 대한 사양은 Table 1에 나타나 있다. 먼저 지상관측 타워 지점은 Fig. 2에서 보이는 바와 같이 각각의 관측장비가 지상관측 타워에 설치되어 있다. 지상관측의 다양한 목적 중에서 항우연의 주요 목적인 위성 부가산출물 검증을 위해서, 그림에서 보는 바와 같이 FLOX 초분광 관측기기 두 대를 각각 타워의 상단(상향) 그리고 타워에서 왼쪽(남쪽)으로 펼쳐진 암(하향)되어 있다. 초분광 관측기기에서 중요한 부분은 상향의 경우 field of view가 180°, 하향의 경우에는 20°로 hemispherical directional reflectance 관측이 가능하다. 이는 일반적인 위성의 관측 기하 특성과 유사하기 때문에 위성관측 산출물 및 부가산출물 검증에 매우 용이하다는 것을 알 수 있다(Schaepman-Strub et al., 2006). 그리고 지표 논벼 지점에 대한 탄소 플럭스 관측을 위해 에디 공분산(eddy covariance) 관측기기(3차원 풍속계, CO2, H2O 가스분석기)가 설치되어 있다. Fig. 3는 에디 공분산에서 산출된 CO2와 잠열(latent heaf) 플럭스에 대한 일일 변화를 보여준다. 그림에서 보여지는 것과 같이 추수 이후 겨울 동안은 낮은 온도로 인해 토양에서의 CO2 방출과 증발량이 매우 낮게 나타난다.
- 그리고 기본적인 기상관측뿐만 아니라, 순복사관측, 적외 온도 관측 및 광합성유효 복사관측도 가능하다. 또한, 대기 관측 지점의 경우에는 Fig. 4에서 보이는 바와 같이 POM-02 지상 관측기기와 대기환경 관측을 위한 스카이 카메라가 설치되어 있다. POM-02 대기복사계는 태양 주변광 및 직달 분광 강도를 측정하는 장치로, 대기 중의 먼지입자 크기 및 농도를 추정할 수 있다. 11개의 파장으로 관측을 하며, 직달광/산란광의 측정함으로써 에어로솔 분포 계산이 가능하다(Uchiyama et al., 2018). Fig. 5는 POM-02 자료를 이용하여 산출한 파장별(500 nm와 675 nm) 에어러솔 광학 두께(aerosol optical depth)에 대한 초도 관측 결과를 보여준다. 그림에서 보여지는 것과 같이 광주과학기술원에 설치된(Oh et al., 2017) CIMEL 대기 복사계와 비교하였을 때, POM-02는 거의 유사한 에어러솔 광학 특성을 보여준다. 특히, 나주에 위치한 전남농업기술원과 광주과학기술원 간의 공간적인 거리차가 22 km임에도 불구하고 높은 상관 특성을 보인다. 대부분의 산점도의 값의 범위가 0.2-0.3에 있으며, 일부 높은 사례에 대해서도 유사한 특성을 보여준다.
- 끝으로, Fig. 6는 항우연에서 개발한 지상관측사이트 관측장비 소개 및 관측 자료 배포를 위한 웹 서비스(https://www.kari.re.kr/ngos/main/main.do) 메인 화면 이미지를 보여준다. 웹 서비스 사이트에서는 현재 나주 지상관측사이트에 설치되어 있는 관측기기 및 관측 자료에 대한 현황 자료를 제공하며, 관측하는 모든 자료는 우선 기관별 업무협약을 통해 제한된 관련기관들에게 배포할 예정이고 향후 웹 페이지 개선을 통해 최종적으로 모든 사용자에게 단계적으로 개방할 계획이다. 기관 사용자에 배포될 시기는 웹 서비스 개선이 완료되는 2023년 말로 예정하고 있으며, 일반사용자 활용 방안에 대한 부분은 주무부처와 협의하여 결정할 예정이다.
2. 지상관측 타워 및 관측 자료
- 나주 지상관측사이트 공간 정보는 Fig. 1에서 보여지는 봐와 같이 위도 35.027° N, 경도 126.822° E 전라남도 나주시 전남농업기술원 지역이다. 지상관측 타워 지점에 대한 대표 토지피복은 논벼 재배 지역이며, 관측타워를 중심으로 약 100×100 m의 균질한 벼 재배지역을 가진다. 대기관측 지점은 앞에서 언급한 봐와 같이 지상관측 타워 지점으로 550 m 정도 떨어져 있으나, 지상관측사이트의 공간적인 대기 특성을 대표하는 데는 큰 무리가 없다.
3. 공간적 범위
- 나주 지상관측사이트 관측 자료는 2020년 1월부터 현재까지 실시간으로 초분광반사도, 대기복사, 탄소순환 및 기상을 관측 중이다. 각각의 지상관측 특성에 따라 시간해상도를 크게 초 단위에서 시간 단위 해상도로 구별될 수 있다(Table 1).
4. 시간적 범위
-
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Funding Information
This work was supported by the “Development of Application Technologies and Supporting System for Microsatellite Constellation” project through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. 2021M1A3A4A11032019).
-
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study will be openly available in KARI at https://www.kari.re.kr/ngos/main/main.do.
Notes





- Oh SH, Kim J, Shon ZH, Bae MS (2017) Assessing the altitudinal potential source contribution function of aerosol optical depth in the West Coast of Korean Peninsula during the DRAGON-KORUS-AQ Campaign. J Korean Soc Atmos Environ 33(1):19–30Article
- Schaepman-Strub G, Schaepman ME, Painter TH, Dangel S, Martonchik JV (2006) Reflectance quantities in optical remote sensing-Definitions and case studies. Remote Sens Environ 103(1):27–42Article
- Uchiyama A, Matsunaga T, Yamazaki A (2018) The instrument constant of sky radiometers (POM-02) – Part 1: calibration constant. Atmos Meas Tech 11(9):5363–5388Article
- Xu J, Zhang YL, Wei Z (2019) Improvement and verification of a satellite-based global evapotranspiration algorithm using ground-based tower measurements. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 23(11):4705–4719
References
Appendix
| Sort | Title | Subcategory#1 | Subcategory#2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Essential | Field | NGOS ground measurement | https://www.kari.re.kr/ngos/main/main.do |
| *DOI name | https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2023.0012 | ||
| *Category | Land (Rice Paddy) | ||
| Abstract | |||
| *Temporal Coverage | 2020 to current | ||
| *Spatial Coverage | (Latitude) 35.027° N | ||
| (Longitude) 126.822° E | |||
| *Personnel | Jong-sung Ha | ||
| Jong-Min Yeom | |||
| Korea Aerospace Research Institute | |||
| Jeonbuk National University | |||
| jongsung@kari.re.kr; jmyeom@jbnu.ac.kr | |||
| *CC License | CC BY-NC | ||
| Optional | *Project | Development of Application Technologies and Supporting System for Microsatellite Constellation | 2021M1A3A4A11032019 |
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 GAIDAS
GAIDAS
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite